What is the schema in Snowflake?
Schemas and databases used for organizing data stored in the Snowflake. A schema is a logical grouping of database objects such as tables, views, etc. The benefits of using Snowflake schemas are it provides structured data and uses small disk space.
What are the benefits of the Snowflake Schema?
- In a denormalized model, we use less disk space.
- It provides the best data quality.
Differentiate Star Schema and Snowflake Schema?
Both Snowflake and Star Schemas are identical, yet the difference exists in dimensions. In Snowflake, we normalise only a few dimensions, and in a star schema, we denormalise the logical dimensions into tables.
What kind of SQL does Snowflake use?
Snowflake supports the most common standardized version of SQL, i.e., ANSI for powerful relational database querying.
What are the cloud platforms currently supported by Snowflake?
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- Microsoft Azure (Azure)
What ETL tools do you use with Snowflake?
Following are the best ETL tools for Snowflake
- Matillion
- Blendo
- Hevo Data
- StreamSets
- Etleap
- Apache Airflow
Snowflake Advanced Interview Questions
Explain zero-copy cloning in Snowflake?
In Snowflake, Zero-copy cloning is an implementation that enables us to generate a copy of our tables, databases, schemas without replicating the actual data. To carry out zero-copy in Snowflake, we have to use the keyword known as CLONE. Through this action, we can get the live data from the production and carry out multiple actions.
Explain “Stage” in the Snowflake?
In Snowflake, the Stage acts as the middle area that we use for uploading the files. Snowpipe detects the files once they arrive at the staging area and systematically loads them into the Snowflake.
Following are the stages supported by the snowflake:
- Table Stage
- User Stage
- Internal Named Stage
Explain data compression in Snowflake?
All the data we enter into the Snowflake gets compacted systematically. Snowflake utilizes modern data compression algorithms for compressing and storing the data. Customers have to pay for the packed data, not the exact data.
How do we secure the data in the Snowflake?
Data security plays a prominent role in all enterprises. Snowflake adapts the best-in-class security standards for encrypting and securing the customer accounts and data that we store in the Snowflake. It provides the industry-leading key management features at no extra cost:
Explain Snowflake Time Travel?
Snowflake Time Travel tool allows us to access the past data at any moment in the specified period. Through this, we can see the data that we can change or delete. Through this tool, we can carry out the following tasks:
Restore the data-associated objects that may have lost unintentionally.
For examining the data utilization and changes done to the data in a specific time period.
Duplicating and backing up the data from the essential points in history.
What is the database storage layer?
Whenever we load the data into the Snowflake, it organizes the data into the compressed, columnar, and optimized format. Snowflake deals with storing the data that comprises data compression, organization, statistics, file size, and other properties associated with the data storage. All the data objects we store in the Snowflake are inaccessible and invisible. We can access the data objects by executing the SQL query operation through Snowflake.
Explain Fail-safe in Snowflake?
Fail-safe is a modern feature that exists in Snowflake to assure data security. Fail-safe plays a vital role in the data protection lifecycle of the Snowflake. Fail-safe provides seven days of additional storage even after the time travel period is completed.
Explain Virtual warehouse?
In Snowflake, a Virtual warehouse is one or more clusters endorsing users to carry out operations like queries, data loading, and other DML operations. Virtual warehouses approve users with the necessary resources like temporary storage, CPU for performing various snowflake operations.
Explain Data Shares?
Snowflake Data sharing allows organizations to securely and immediately share their data. Secure data sharing enables sharing of the data between the accounts through Snowflake secure views, database tables.
What are the various ways to access the Snowflake Cloud data warehouse?
We can access the Snowflake data warehouse through:
- ODBC Drivers
- JDBC Drivers
- Web User Interface
- Python Libraries
- SnowSQL Command-line Client
What are the advantages of Snowflake Compression?
Following are the advantages of the Snowflake Compression:
- Storage expenses are lesser than original cloud storage because of compression.
- No storage expenditure for on-disk caches.
- Approximately zero storage expenses for data sharing or data cloning.
Differentiate Fail-Safe and Time-Travel in Snowflake?
| Time-Travel | Fail-Safe |
| According to the Snowflake edition, account or object particular time travel setup, users can retrieve and set the data reverting to the history. | Fail-Safe, the User does not have control over the recovery of data valuable merely after completing the period. In this context, only Snowflake assistance can help for 7 days. Therefore if you set time travel as six days, we retrieve the database objects after executing the transaction + 6 days duration. |
Explain Snowpipe in Snowflake?
Snowpipe is a cost-efficient and constant service that we use for loading the data into the Snowflake. Snowpipe systematically loads data from the files as soon as they are attainable on the stage. Snowpipe eases the data loading process by loading the data into the micro-batches and shapes data for analysis.
What are the advantages of the Snowpipe?
Following are the Snowpipe advantages:
- Live insights
- User-friendly
- Cost-efficient
- Resilience
Explain Micro Partitions?
Snowflake comes along with a robust and unique kind of data partitioning known as micro partitioning. Data that exists in the Snowflake tables are systematically converted into micro partitions. Generally, we perform Micro partitioning on the Snowflake tables.
Explain Columnar database?
The columnar database is opposite to the conventional databases. It saves the data in columns in place of rows, eases the method for analytical query processing and offers more incredible performance for databases. Columnar database eases analytics processes, and it is the future of business intelligence.
How to create a Snowflake task?
To create a Snowflake task, we have to use the “CREATE TASK” command. Procedure to create a snowflake task:
CREATE TASK in the schema.
USAGE in the warehouse on task definition.
Run SQL statement or stored procedure in the task definition.
How do we create temporary tables?
To create temporary tables, we have to use the following syntax:
Create temporary table mytable (id number, creation_date date);
Where do we store data in Snowflake?
Snowflake systematically creates metadata for the files in the external or internal stages. We store metadata in the virtual columns, and we can query through the standard “SELECT” statement.
39. Does Snowflake use Indexes?
No, Snowflake does not use indexes. This is one of the aspects that set the Snowflake scale so good for the queries.
How is Snowflake distinct from AWS?
Snowflake offers storage and computation independently, and storage cost is similar to data storage. AWS handles this aspect by inserting Redshift Spectrum, which enables data querying instantly on S3, yet not as continuous as Snowflake.
How do we execute the Snowflake procedure?
Stored procedures allow us to create modular code comprising complicated business logic by adding various SQL statements with procedural logic. For executing Snowflake procedure, carry out the below steps:
- Run a SQL statement
- Extract the query results
- Extract the result set metadata
Does Snowflake maintain stored procedures?
Yes, Snowflake maintains stored procedures. The stored procedure is the same as a function; it is created once and used several times. Through the CREATE PROCEDURE command, we can create it and through the “CALL” command, we can execute it. In Snowflake, stored procedures are developed in Javascript API. These APIs enable stored procedures for executing the database operations like SELECT, UPDATE, and CREATE.
Is Snowflake OLTP or OLAP?
Snowflake is developed for the Online Analytical Processing(OLAP) database system. Subject to the usage, we can utilize it for OLTP(Online Transaction processing) also.
How is Snowflake distinct from Redshift?
Both Redshift and Snowflake provide on-demand pricing but vary in package features. Snowflake splits compute storage from usage in its pricing pattern, whereas Redshift integrates both.
What is the use of the Cloud Services layer in Snowflake?
The services layer acts as the brain of the Snowflake. In Snowflake, the Services layer authenticates user sessions, applies security functions, offers management, performs optimization, and organizes all the transactions.
What is the use of the Compute layer in Snowflake?
In Snowflake, Virtual warehouses perform all the data handling tasks. Which are multiple clusters of the compute resources. While performing a query, virtual warehouses extract the least data needed from the storage layer to satisfy the query requests.
What is Unique about Snowflake Cloud Data Warehouse?
Snowflake is cloud native (built for the cloud).So, It takes advantage of all the good things about the cloud and brings exciting new features like,
- Auto scaling
- Zero copy cloning
- Dedicated virtual warehouses
- Time travel
- Military grade encryption and security
- Robust data protection features
Snowflake is a poetry. It’s beautifully crafted with smart defaults –
- All the data is compressed by default
- All the data is encrypted
- Its Columnar, thereby making the column level analytical operations a lot faster
Not to mention the number of innovations in the product – eg. Intelligent Services layer, data shares, tasks & streams. Snowflake also has a simple and transparent pricing, which makes it very easier even for smaller businesses to afford a cloud data warehouse
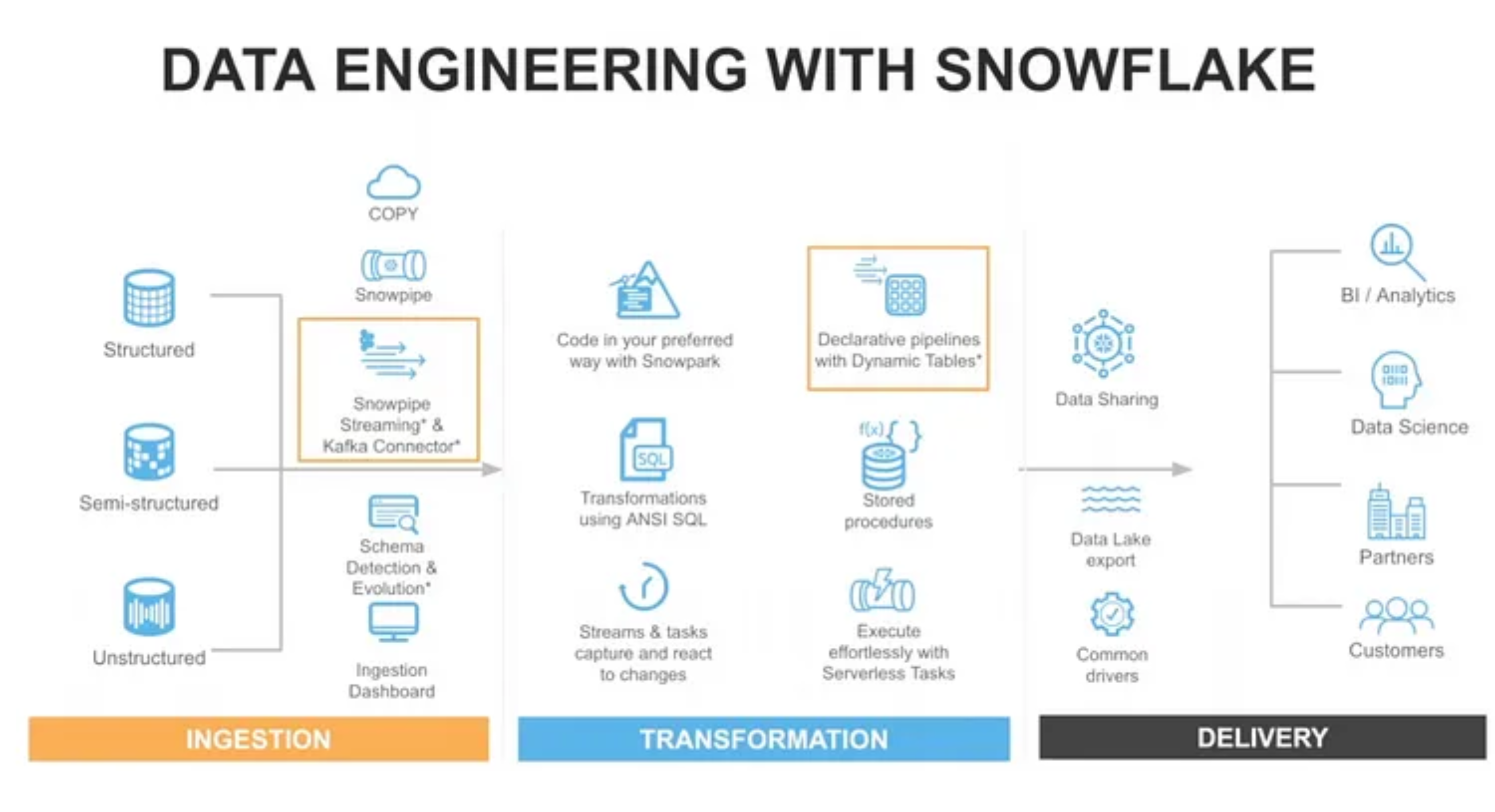
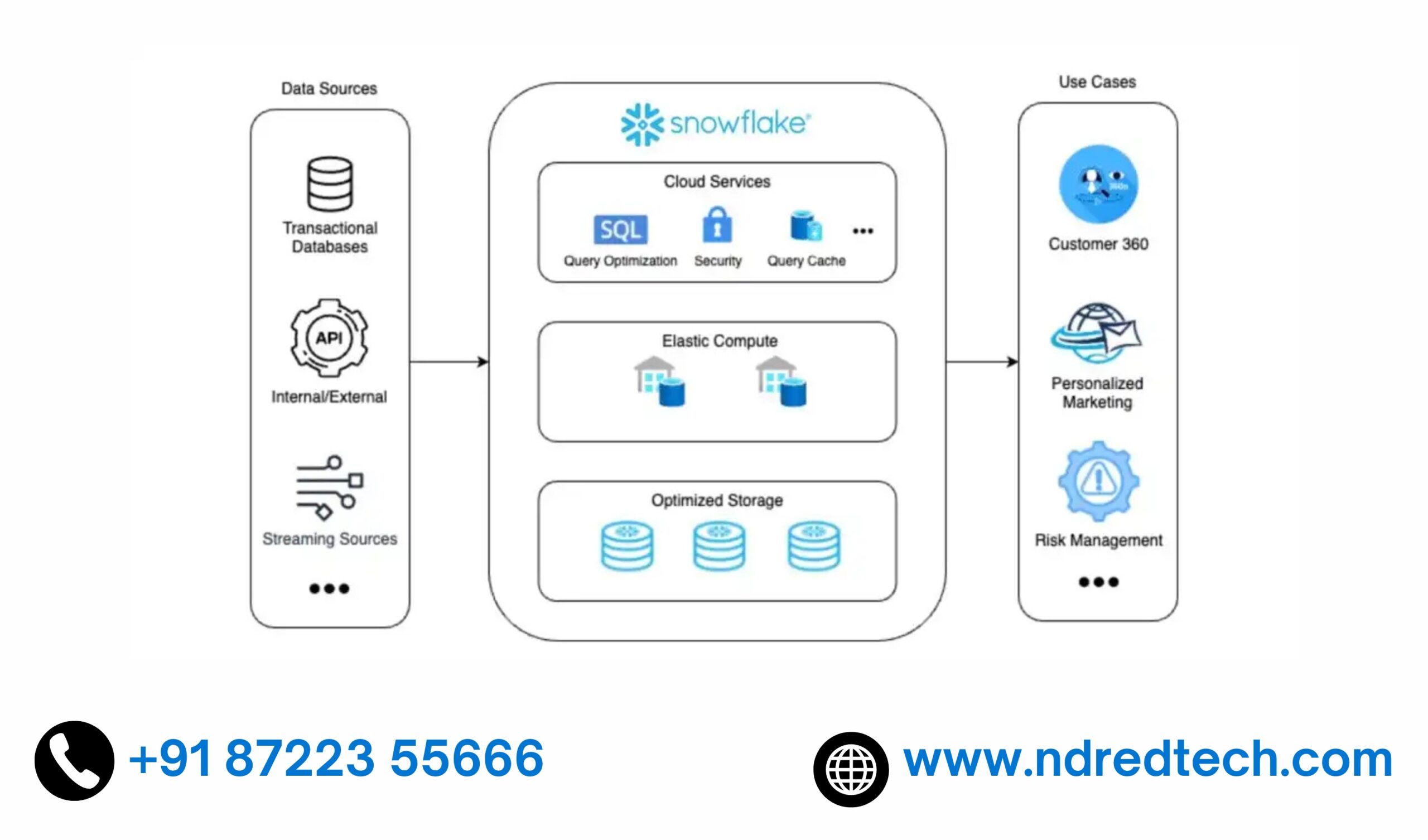
What is Snowflake Architecture ?
Snowflake is built on a patented, multi-cluster, shared data architecture created for the cloud. Snowflake architecture is comprised of storage, compute, and services layers that are logically integrated but scale infinitely and independent from one another
What does the Storage Layer do in Snowflake ?
The storage layer stores all the diverse data, tables and query results in Snowflake. The Storage Layer is built on scalable cloud blob storage (uses the storage system of AWS, GCP or Azure). Maximum scalability, elasticity, and performance capacity for data warehousing and analytics are assured since the storage layer is engineered to scale completely independent of compute resources
What does the Compute Layer do in Snowflake ?
All data processing tasks within Snowflake are performed by virtual warehouses, which are one or more clusters of compute resources. When performing a query, virtual warehouses retrieve the minimum data required from the storage layer to fullfil the query requests
What does the Cloud Services Layer do in Snowflake ?
The services layer is the brain of Snowflake. The services layer for Snowflake authenticates user sessions, provides management, enforces security functions, performs query compilation and optimization, and coordinates all transactions