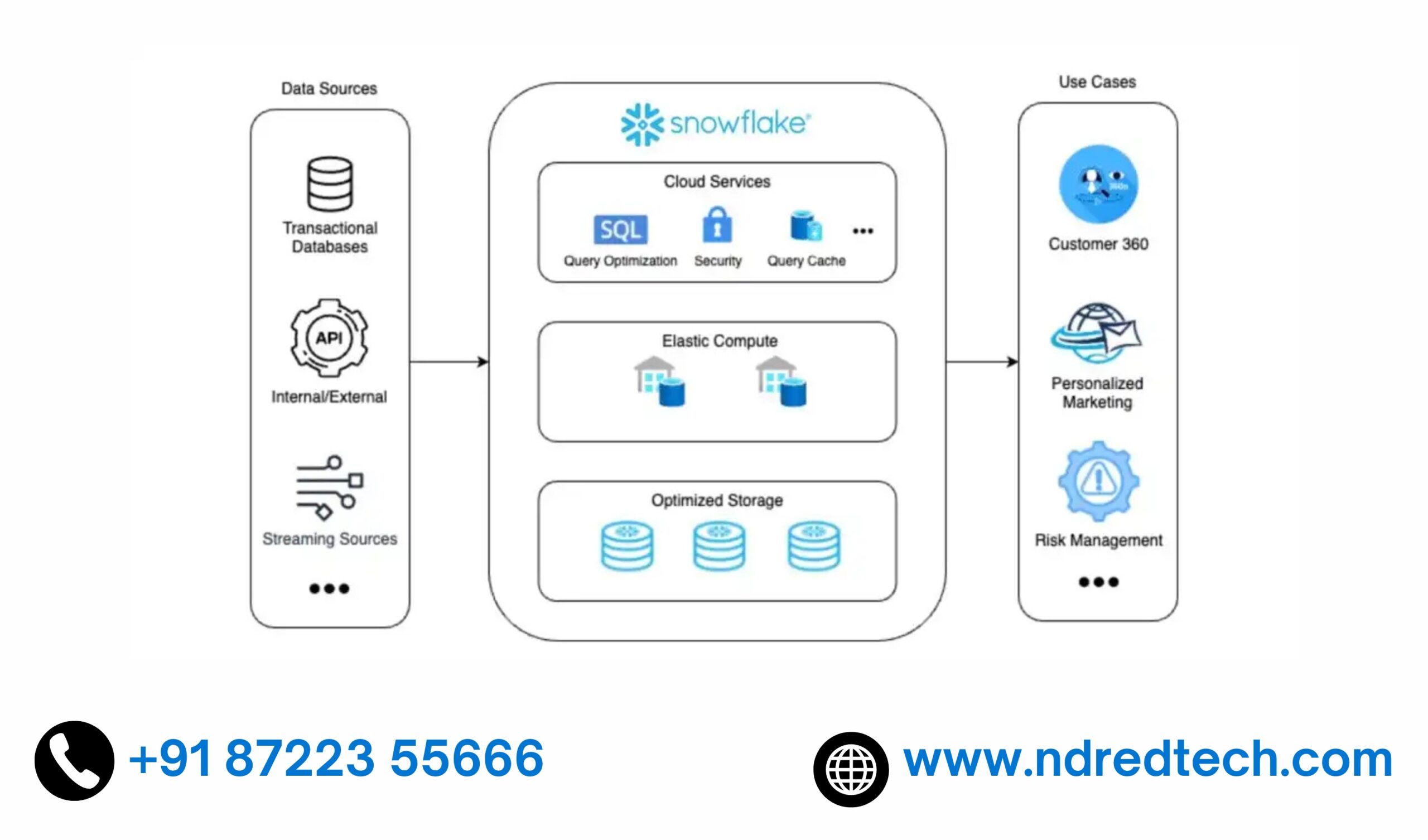
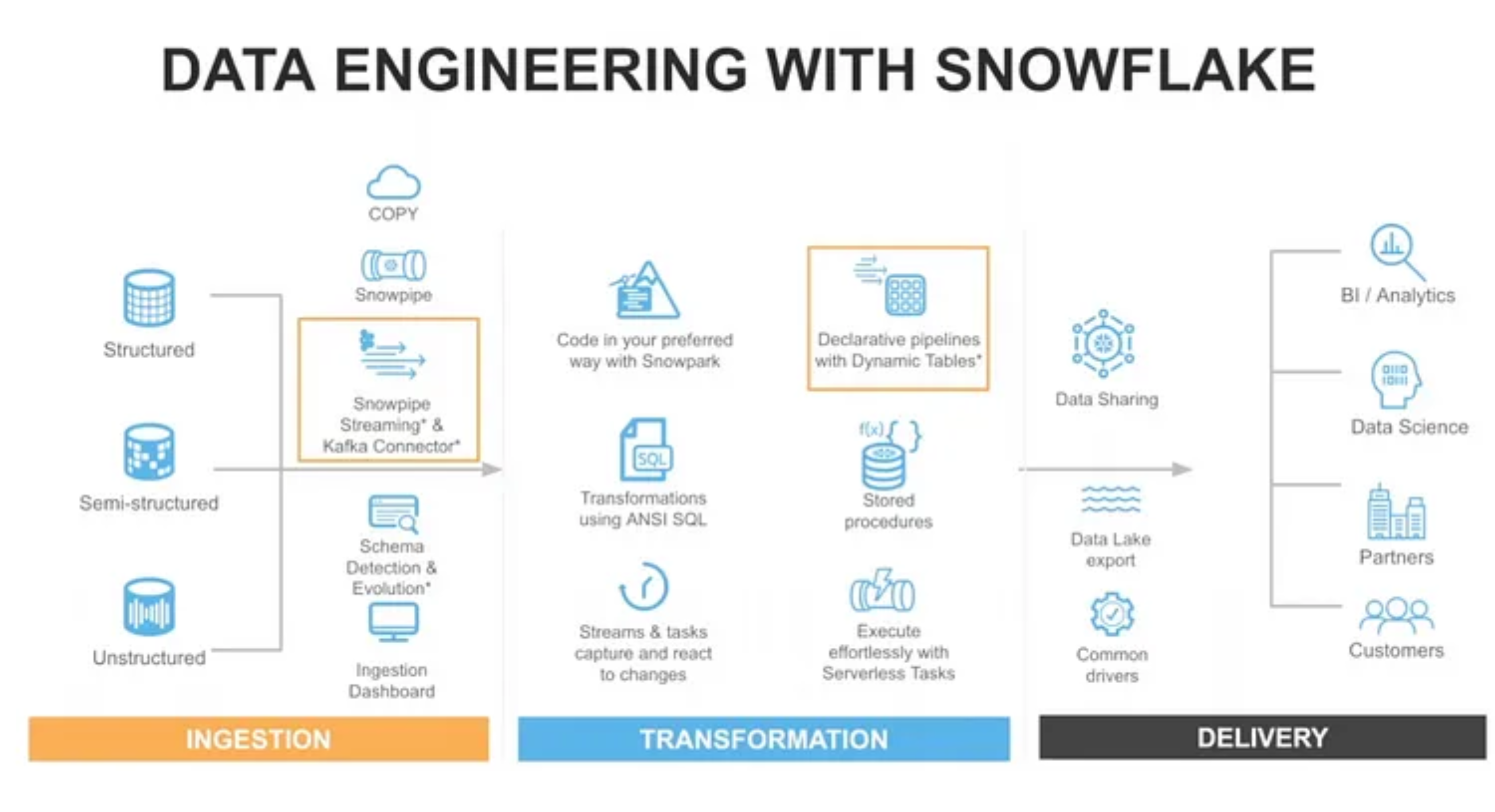
What is Data Sharing in Snowflake?
Data Sharing in Snowflake enables organizations to share live, real-time data with multiple consumers without physically copying or transferring data. This ensures efficient data collaboration with external or internal teams.
Key Features of Data Sharing:
- No Data Duplication: Shared data remains in the provider’s account and does not consume storage in the consumer’s account.
- Live & Real-Time: Any updates made by the data provider are immediately visible to the data consumer.
- Cross-Cloud & Cross-Region Support: Snowflake enables secure cross-cloud and cross-region data sharing.
- No ETL Required: No need to extract, transform, or load data between accounts.
How Does Snowflake Data Sharing Work?
- Data Provider creates a share object using
CREATE SHARE. - The provider grants access to specific databases, schemas, or tables.
- Data Consumer can then create a database from the share to access the data.
Example of Data Sharing in Snowflake:
Step 1: Provider Creates a Share
CREATE SHARE sales_data_share;
GRANT USAGE ON DATABASE sales_db TO SHARE sales_data_share;
GRANT SELECT ON TABLE sales_db.orders TO SHARE sales_data_share;Step 2: Provider Grants Access to a Consumer Account
ALTER SHARE sales_data_share ADD ACCOUNT = 'ORG12345.ACCOUNT1';Step 3: Consumer Creates a Database from the Shared Data
CREATE DATABASE sales_db_from_share FROM SHARE provider_account.sales_data_share;What is Cloning in Snowflake?
Cloning in Snowflake allows users to create instant, metadata-based copies of databases, schemas, or tables without duplicating data. It is useful for:
- Creating development/test environments without affecting production data.
- Running analytical queries on a point-in-time snapshot.
- Experimenting with schema changes without impacting live data.
Key Features of Cloning in Snowflake:
- Zero-Copy Cloning: No actual data duplication occurs; only metadata is copied.
- Instantaneous: Clones are created almost instantly, regardless of size.
- Independent Changes: Changes in a cloned table do not affect the original table (except for time travel references).
- Uses Snowflake’s Storage Optimization: New data is stored only when changes are made.
Example of Cloning in Snowflake:
Cloning a Table
CREATE TABLE cloned_orders CLONE sales_db.orders;Cloning an Entire Schema
CREATE SCHEMA cloned_schema CLONE sales_db.sales_schema;Cloning a Database
CREATE DATABASE cloned_db CLONE sales_db;Key Differences: Data Sharing vs. Cloning
| Feature | Data Sharing | Cloning |
|---|---|---|
| Storage | No storage cost for consumer | Uses storage only when changes are made |
| Data Modification | Read-only for consumer | Can modify cloned data independently |
| Performance | No performance impact on provider | Clones perform like regular tables |
| Use Case | Sharing live data across accounts | Creating isolated copies for testing & analytics |
| Time Travel | Not available for consumer | Supports Time Travel |
When to Use Data Sharing vs. Cloning?
Use Data Sharing When:
- You need to share real-time data with another account.
- You want to avoid data duplication & storage costs.
- You need secure data collaboration with external teams.
Use Cloning When:
- You want to create a test/dev environment without modifying production data.
- You need a snapshot of data for analysis.
- You want to experiment with schema changes without affecting live data.