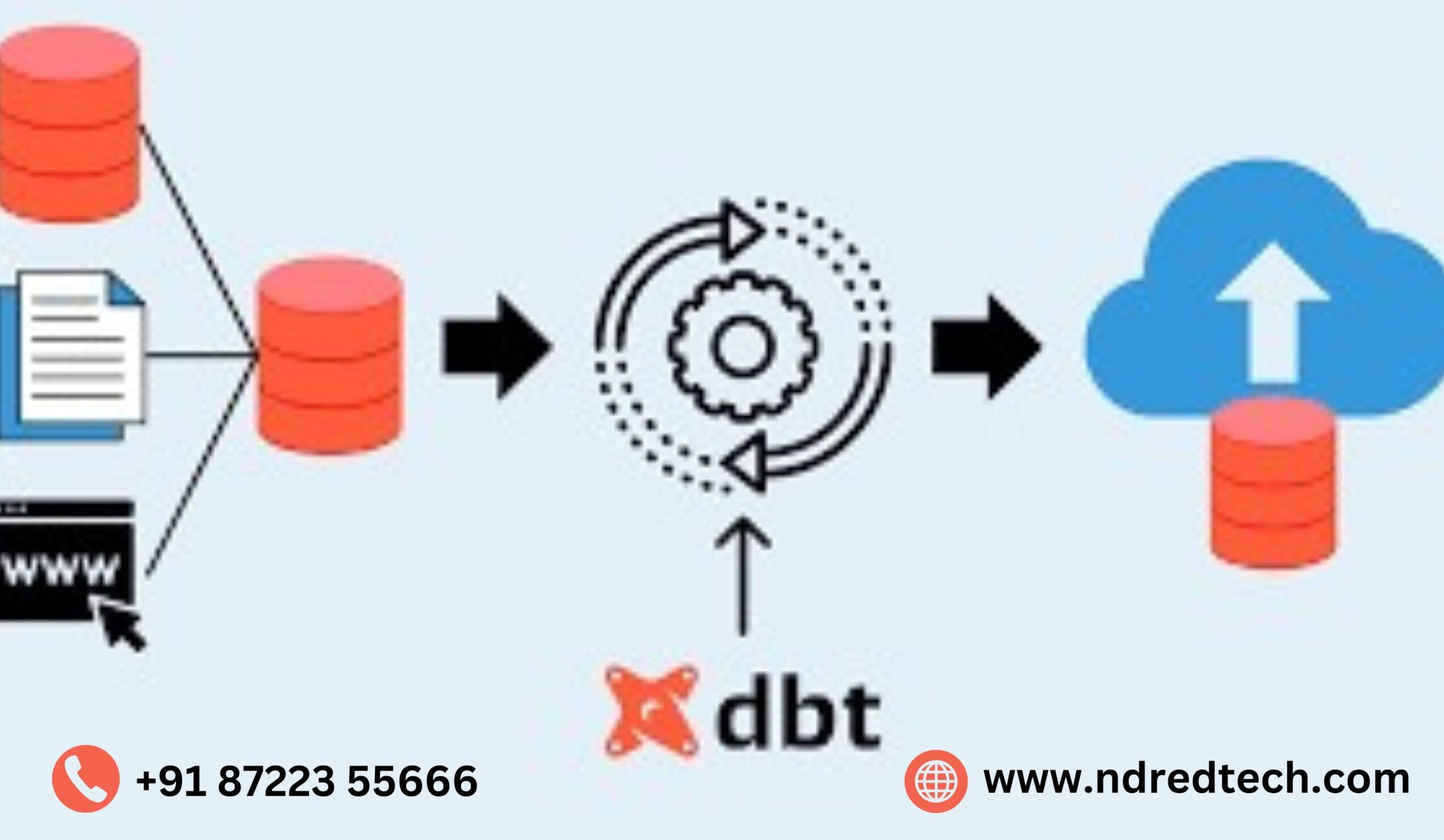
1.Understanding Traditional ETL
Traditional ETL follows a three-step process:
- Extract: Data is pulled from various sources (databases, APIs, files).
- Transform: Data is processed, cleaned, and structured outside the database (often in an ETL tool or script).
- Load: The transformed data is loaded into a data warehouse for analytics.
Popular Traditional ETL Tools:
- Informatica
- Talend
- Apache Nifi
- SSIS (SQL Server Integration Services)
Challenges of Traditional ETL:
- Expensive infrastructure for transformation outside the warehouse.
- Long development cycles with heavy dependency on engineering teams.
- Harder to scale as data volume increases.
2.Understanding DBT (Data Build Tool)
DBT takes a different approach by focusing on ELT (Extract, Load, Transform):
- Extract & Load: Raw data is first extracted and loaded into a data warehouse (Snowflake, BigQuery, Redshift).
- Transform: Instead of external processing, SQL-based transformations occur inside the warehouse using DBT models.
Why DBT is Different:
- SQL-based: Business analysts and data teams can write transformations without deep engineering skills.
- Modular Approach: Reusable, version-controlled, and collaborative transformation scripts.
- Performance Optimization: Leverages modern cloud-based warehouses for scalability.
Popular Use Cases of DBT:
- Data transformation in modern ELT pipelines.
- Creating and maintaining data models in Snowflake, BigQuery, or Redshift.
- Automating and scheduling data transformations.
3.Key Differences Between DBT and Traditional ETL
| Feature | Traditional ETL | DBT (ELT) |
| Processing Location | Outside the warehouse | Inside the warehouse (SQL-based) |
| Complexity | Requires engineering skills | SQL-friendly for analysts |
| Cost Efficiency | Expensive due to external compute | Cost-effective using warehouse power |
| Scalability | Limited by ETL tool capacity | Scales with cloud warehouses |
| Development Speed | Slower, heavy engineering effort | Faster, modular development |
| Collaboration | Limited version control | Git-based version control |
4.Which One Should You Choose?
- Use Traditional ETL if you have legacy systems, complex transformations requiring external processing, or on-premise infrastructure.
- Use DBT if you are working with cloud-based data warehouses, need a scalable and efficient transformation process, and want a SQL-based approach for self-service analytics.